Concussion
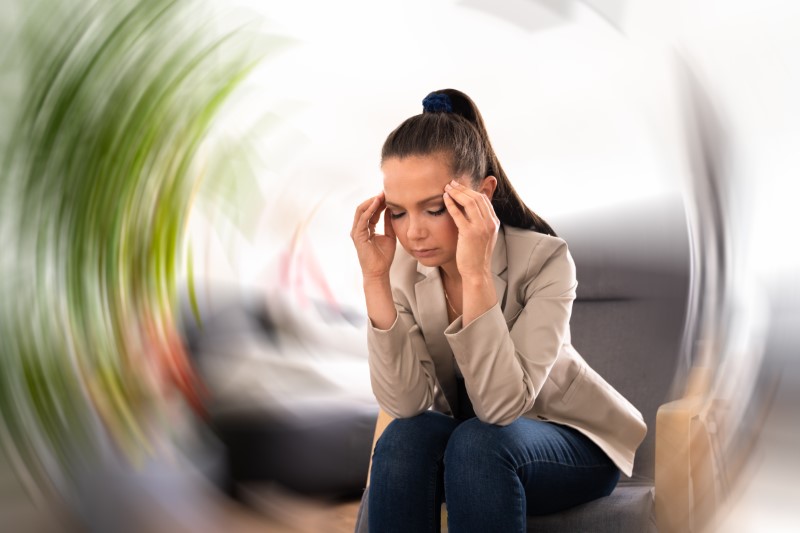
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) that occurs when a forceful impact or sudden movement causes the brain to shake inside the skull. This can lead to temporary changes in brain function, affecting balance, vision, memory, and coordination.
Causes
- Direct blow to the head (e.g., sports injuries, falls, car accidents)
- Sudden jolt or whiplash-like motion causing an indirect shaking of the brain
- Contact with a hard surface (e.g., hitting the ground or an object)
Diagnosis
- Clinical evaluation of symptoms and medical history
- Neurological and cognitive testing (memory, concentration, balance)
- Vestibular and ocular assessments for dizziness and vision changes
- Imaging (CT or MRI) in severe or complicated cases
Treatment
- Balance and vestibular therapy to improve dizziness and coordination
- Vision therapy for eye tracking and focus issues
- Cervical spine treatment to address neck pain and headaches
- Gradual return-to-play/activity program to restore endurance and function
- Education on symptom management and activity modification
Recovery
- Most mild concussions resolve within 7-14 days with proper management
- Some cases may take 3-4 weeks, especially with persistent symptoms
- Post-concussion syndrome (PCS) may extend recovery beyond 4 weeks
- A structured, supervised return-to-activity plan improves outcomes and reduces the risk of prolonged symptoms